Sodium-ion Battery: How Does it Work? Pros & Cons Explained
The rising demand for affordable, reliable energy storage is reshaping industries. Electric vehicles, renewable energy projects, and smart grids all depend heavily on batteries.
While lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market, growing concerns about cost, supply chains, and environmental impact are pushing industries to explore alternatives. The top alternative to lithium-ion is the sodium-ion battery, which is built from abundant materials and offers a promising solution for future energy storage.
But how do these batteries work, and what are their pros and cons?

How Do Sodium-Ion Batteries Work?
Basically, a sodium-ion battery stores and releases energy by moving sodium ions between two electrodes during charging and discharging. Key components of these a sodium battery include:
- Cathode: This is the positive terminal of the battery. During charging, sodium ions leave the cathode and travel toward the anode.
- Anode: The negative side that receives sodium ions during charging and releases them back to the cathode during discharge.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that allows sodium ions to move between electrodes while blocking electrons.
- Separator: A barrier that prevents the anode and cathode from touching while still allowing ions to pass through.
Charging a Na-ion battery pushes sodium ions from the cathode to the anode using external energy. While you use this battery, the ions flow back to the cathode, producing an electric current.
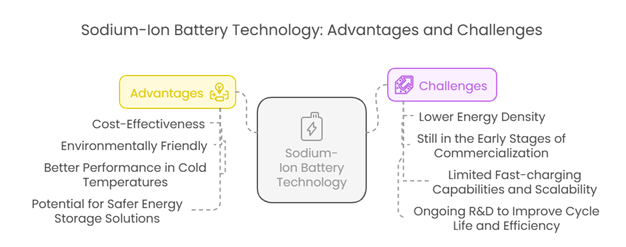
Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion battery technology comes with several advantages, such as:
Cost-effectiveness
Sodium is exceptionally abundant and widely available in the Earth’s crust and oceans, ranking as the sixth most abundant element. This abundance helps lower material costs and makes sodium-ion battery a more affordable option for manufacturers and consumers.
Environmentally Friendly
Lithium extraction usually damages ecosystems and drains water resources. Sodium extraction has a smaller environmental footprint, which reduces the impact associated with building large battery systems.
Better Performance in Cold Temperatures
Sodium-ion batteries demonstrate stable electrochemical performance at low temperatures. They perform well at low temperatures because their electrochemical reactions remain highly efficient even when it’s cold, and the electrolyte formulations are optimized to prevent freezing, ensuring consistent ion movement[1].
Potential for Safer Energy Storage Solutions
The chemical structure and relatively lower energy density of sodium-ion batteries contribute to a reduced risk of thermal runaway. Their material stability enhances safety for residential, industrial, and transportation uses.
Current Limitations and Challenges
Despite its potential, sodium-ion technology still faces several challenges, such as:
Lower Energy Density
Sodium-ion batteries store less energy by weight or volume, which means that you need bigger batteries to store the same amount of energy compared to lithium batteries. This limits their appeal for mobile devices and electric vehicles where manufacturers are inclined toward lightweight solutions.
Still in the Early Stages of Commercialization
While prototypes exist, sodium-ion batteries are still not widely available. Commercial production is still limited, which makes their sourcing a bit difficult.
Limited Fast-charging Capabilities and Scalability
Sodium-ion batteries currently cannot match the rapid charging speeds users expect without risking battery degradation. Scaling the production of these batteries also presents hurdles.
Ongoing R&D to Improve Cycle Life and Efficiency
Researchers are still improving sodium-ion battery materials to extend lifespan and boost performance. However, the implementation of lab innovations for improving cycle life and efficiency of these batteries will take time and investment.
Learn More at The Battery Show Asia 2025
The Battery Show Asia 2025 is the place to be for all the energy storage enthusiasts who want a deeper insight into the future of battery technology. Scheduled from July 15 to 17, 2025, at AsiaWorld-Expo in Hong Kong, this event brings together the brightest minds in the battery, energy storage, and electric vehicle industries.
You can expect to see companies showcasing technologies related to battery manufacturing, energy storage systems, EV solutions, battery recycling, hydrogen, fuel cell technologies, and much more. Expert panels will address critical topics such as battery safety, recycling, design improvements, and new energy mobility trends.

Conclusion
Sodium-ion batteries offer a promising path toward affordable, sustainable energy storage. While challenges remain, ongoing research and growing industry interest point to a strong future.
Join us now at The Battery Show Asia 2025 to learn more about these batteries, connect with experts, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving energy storage field.
Reference
[1] Why Sodium-Ion Batteries Perform Well at Low Temperatures. Available at: https://nadionenergy.com/why-sodium-ion-batteries-perform-well-at-low-temperatures/ (Accessed: 29th, April)


